Dermatology Department
Dermatology is the branch of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of skin, hair, and nail disorders. Dermatologists are medical doctors who specialize in this field and are trained to manage a wide variety of conditions affecting the skin, from cosmetic issues to severe diseases.
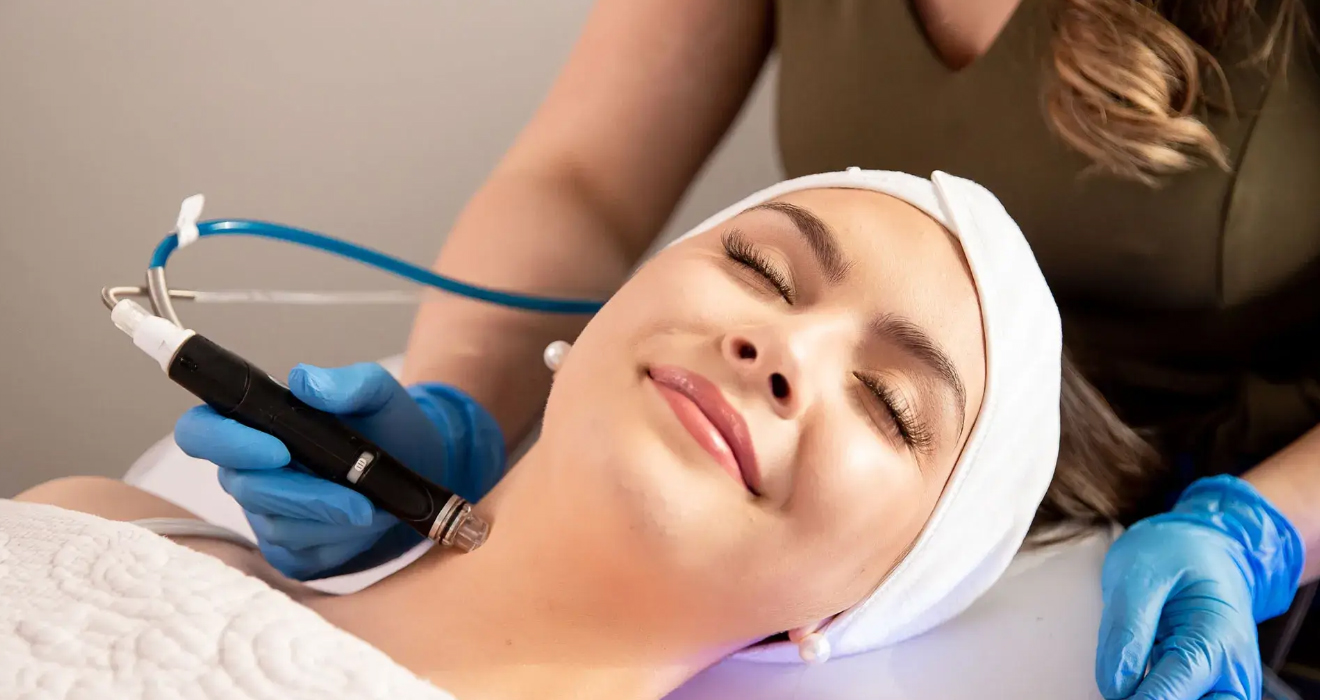


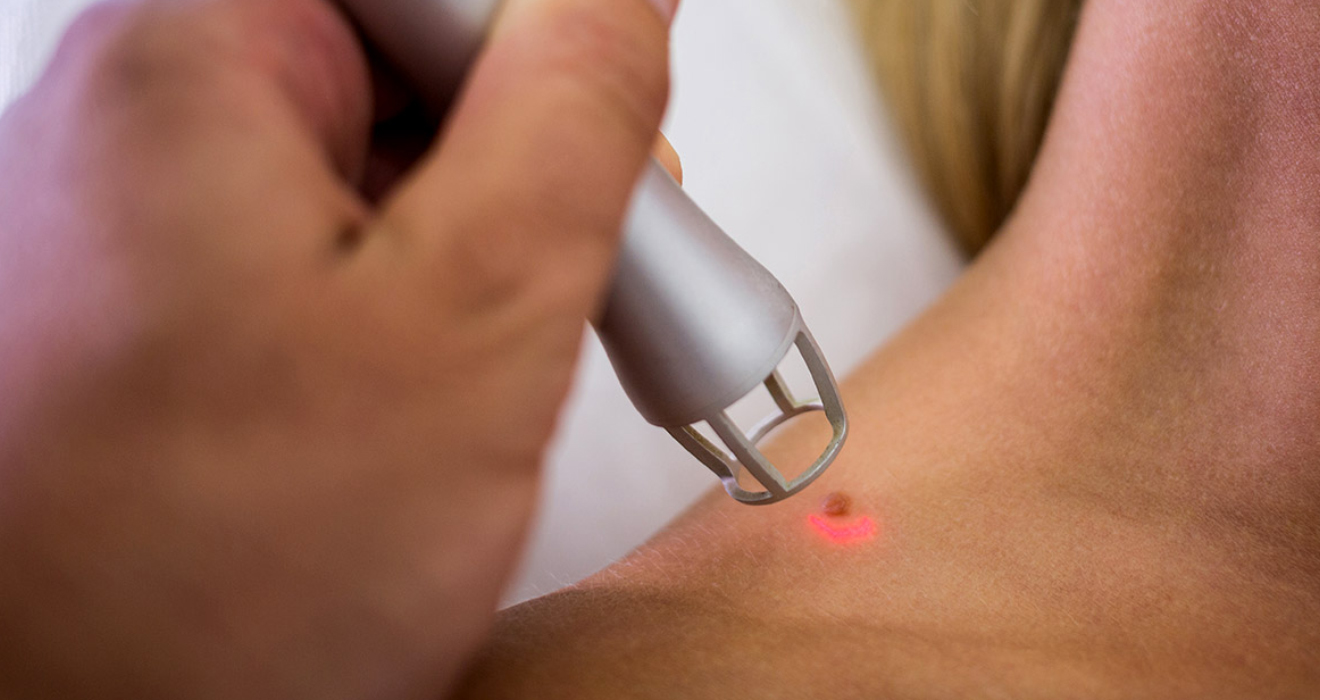
General Dermatology:
- Treatment of common skin conditions like acne, eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis.
- Management of infections caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
- Addressing hair disorders such as alopecia (hair loss) and nail disorders like fungal infections.
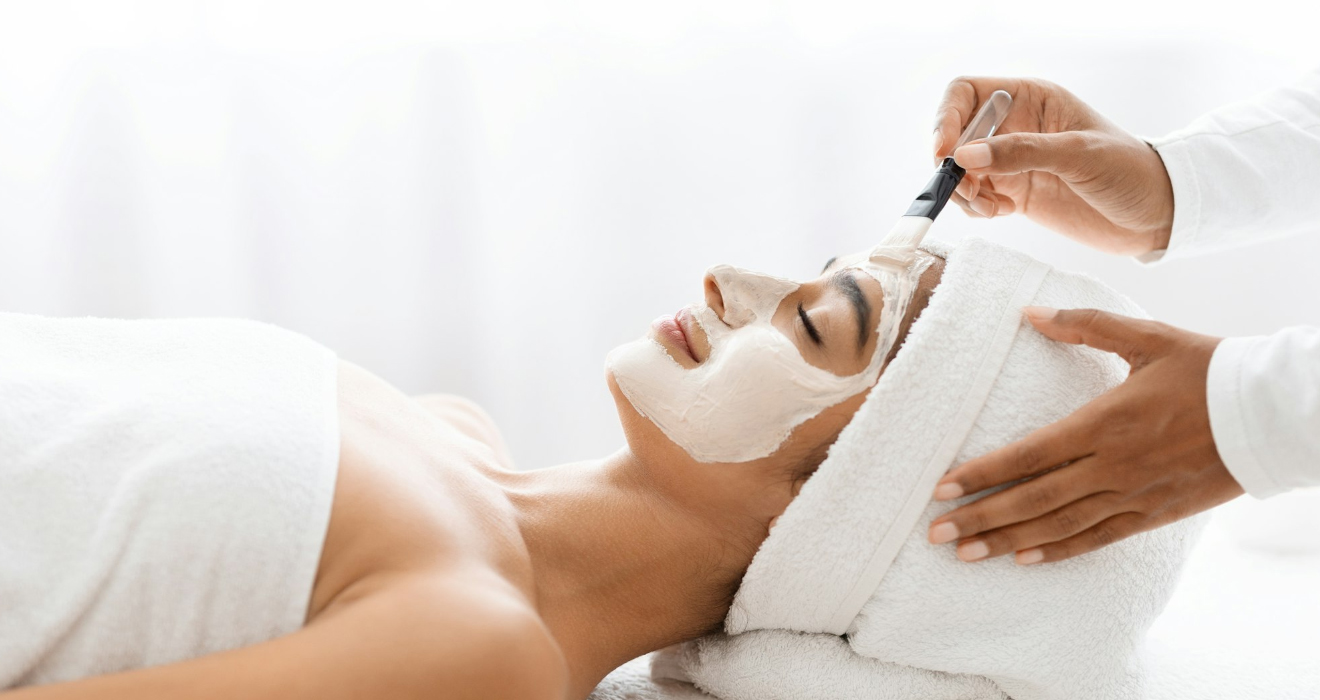
Cosmetic Dermatology:
- Procedures to improve the appearance of the skin, including Botox injections, fillers, chemical peels, and laser treatments.
- Treatments for hyperpigmentation, scars, wrinkles, and other cosmetic concerns.
Dermatopathology:
- Study and diagnosis of skin diseases at a microscopic level.
- Biopsy and analysis of skin samples to diagnose conditions like skin cancer, inflammatory skin diseases, and infectious skin diseases.
Pediatric Dermatology:
- Specializes in treating skin conditions in infants, children, and adolescents.
- Common issues include birthmarks, eczema, and genetic skin disorders.
Mohs Surgery:
- A specialized surgical technique for treating skin cancer.
- Involves the removal of cancerous tissues layer by layer, examining each layer under a microscope until no cancer cells remain.
Immunodermatology:
- Focuses on skin disorders related to the immune system, such as lupus, pemphigus, and other autoimmune skin diseases.
- Acne: A condition characterized by pimples, blackheads, and cysts, commonly occurring on the face, chest, and back.
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): A chronic condition causing inflamed, itchy, and red skin.
- Psoriasis: An autoimmune disease that causes red, scaly patches on the skin.
- Rosacea: A chronic condition that causes redness and visible blood vessels on the face.
- Skin Cancer: Includes basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
- Dermatitis: Inflammation of the skin, which can be caused by allergies, irritants, or other factors.
- Warts: Skin growths caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV).
- Fungal Infections: Includes athlete’s foot, ringworm, and yeast infections.
- Hair Disorders: Such as alopecia areata and pattern hair loss.
- Skin Biopsy: Removal of a small section of skin for microscopic examination to diagnose skin conditions, including cancer.
- Dermatoscopy: Use of a dermatoscope to examine skin lesions and moles more closely.
- Patch Testing: Used to identify allergens causing contact dermatitis.
- Blood Tests: To diagnose systemic diseases with skin manifestations.
- Imaging Studies: Such as MRI or CT scans for deeper tissue analysis in certain skin conditions.
- Topical Treatments:
- Creams, ointments, and lotions containing medications such as steroids, retinoids, or antibiotics.
- Oral Medications:
- Antibiotics, antifungals, immunosuppressants, and systemic steroids.
- Phototherapy:
- Use of ultraviolet light to treat conditions like psoriasis and eczema.
- Surgical Procedures:
- Removal of skin lesions, moles, cysts, and skin cancer.
- Mohs surgery for skin cancer.
- Laser Therapy:
- Used for treating various skin issues, including acne scars, pigmentation disorders, and hair removal.
- Cosmetic Procedures:
- Botox, fillers, chemical peels, and microdermabrasion to enhance skin appearance.
- Diagnosis:
- Identifying skin conditions through visual examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests.
- Treatment Planning:
- Developing individualized treatment plans based on the specific skin condition and patient needs.
- Patient Management:
- Monitoring patient progress and adjusting treatments as necessary.
- Educating patients on skincare routines and preventive measures.
- Procedures:
- Performing surgical and non-surgical procedures to treat skin conditions.
- Research and Education:
- Staying updated with the latest advancements in dermatology.
- Educating patients and the community about skin health and disease prevention.
- Sun Protection: Encouraging the use of sunscreen and protective clothing to prevent skin cancer and photoaging.
- Skincare Routine: Advising on proper skincare routines to manage conditions like acne and eczema.
- Regular Skin Checks: Recommending regular self-examinations and professional skin checks for early detection of skin cancer.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Promoting a healthy diet and lifestyle to improve skin health.
Dermatologists play a crucial role in managing skin health, treating a wide range of conditions, and enhancing the quality of life for patients with skin disorders.
Dermatology Specialist
A dermatology specialist, or dermatologist, is a medical doctor who focuses on diagnosing, treating, and preventing skin, hair, and nail disorders. Dermatologists are trained to handle a wide variety of conditions, ranging from cosmetic issues to serious diseases like skin cancer.
in neurology, and often additional fellowship training in specific subspecialties.

